I hate to make decisions! Ask anyone in my family, and they’ll tell you about daily scenes like this:
“Hey Dad! What do you want for dinner?”
“Ummmm. . .”
“Steve, what would you like to do tonight?”
“I don’t know, honey. What would you like to do?”
In our house, I am famous for presenting endless lists of options: “Okay, we could do A, B, or C, although if we do C, we’d need to decide between x and y. . .”
You get the picture. Wendy is a saint.
Usually, my indecisiveness, while irritating, doesn’t matter that much: world peace doesn’t depend on whether we get takeout from Chipotle or Five Guys. However, some decisions do matter. Sometimes, a choice must be made, and a stand must be taken. How do we do that?
In our New Testament, 1 John is all about Christian decision-making: discerning the truth among competing claims; listening for the Word within the words. From its very first chapter, 1 John engages us with matters of discernment, beginning with how we can know whether or not we are true followers of Christ. Significantly, it is not through our confident conviction in our own righteousness:
If we claim, “We don’t have any sin,” we deceive ourselves and the truth is not in us. But if we confess our sins, he is faithful and just to forgive us our sins and cleanse us from everything we’ve done wrong (1 Jn 1:8-9).
When I was a young believer, persuaded that I had failed at following Jesus and that there was therefore no hope for me, those verses were my lifeline!

Another question for discernment is the nature of the church: What is the true mark of the Christian community? For 1 John, the answer is a single word: LOVE!
“This is the message that you heard from the beginning: love each other” (1 Jn 3:11)
“Little children, let’s not love with words or speech but with action and truth” (1 Jn 3:18).
My favorite Bible passage is 1 John 4:7-8, a text which I believe to be the Golden Text of Scripture. If you are looking for a succinct statement of what the Bible is all about, it is hard to beat this:
Dear friends, let’s love each other, because love is from God, and everyone who loves is born from God and knows God. The person who doesn’t love does not know God, because God is love.
1 John 5:1-5 sums up the connection between love for one another and love for God:
Everyone who believes that Jesus is the Christ has been born from God. Whoever loves someone who is a parent loves the child born to the parent. This is how we know that we love the children of God: when we love God and keep God’s commandments. This is the love of God: we keep God’s commandments. God’s commandments are not difficult, because everyone who is born from God defeats the world. And this is the victory that has defeated the world: our faith. Who defeats the world? Isn’t it the one who believes that Jesus is God’s Son?
Just as the proof of love for God is love for one another, so also love for God and obedience to God’s commandments means love for one another: the two are tightly and inseparably intertwined.

How are we to evaluate Christian preaching and testimony? Once more, 1 John answers with a single word: JESUS! Does this testimony, this sermon, this soundbite proclaim Jesus?
This is how you know if a spirit comes from God: every spirit that confesses that Jesus Christ has come as a human is from God, and every spirit that doesn’t confess Jesus is not from God (1 Jn 4:2-3).
Here, it seems, 1 John is drawing on the testimony of the Gospel of John, specifically on its Prologue:
In the beginning was the Word
and the Word was with God
and the Word was God. . . .
The Word became flesh
and made his home among us.
We have seen his glory,
glory like that of a father’s only son,
full of grace and truth (John 1:1, 14).
In similarly mystical, poetic language, 1 John 5:6-9 relates God’s testimony regarding the Son:
This is the one who came by water and blood: Jesus Christ. Not by water only but by water and blood. And the Spirit is the one who testifies, because the Spirit is the truth. The three are testifying— the Spirit, the water, and the blood—and the three are united in agreement. If we receive human testimony, God’s testimony is greater, because this is what God testified: he has testified about his Son.
In Deuteronomy, a court case requires two or three witnesses (Deut 17:6, 19:15). Just so, 1 John says, there are three witnesses that confirm Jesus as God’s son: the Spirit, the water, and the blood. Once again, it seems likely that the author of 1 John is drawing here on the Fourth Gospel. In John 3:5-6, Jesus tells Nicodemus
I assure you, unless someone is born of water and the Spirit, it’s not possible to enter God’s kingdom. Whatever is born of the flesh is flesh, and whatever is born of the Spirit is spirit.
So being “born of water” seems to refer to the waters of the womb, and to natural, physical birth. The reference to the blood seems to be a reference back to 1 John 1:7:
But if we live in the light in the same way as he is in the light, we have fellowship with each other, and the blood of Jesus, his Son, cleanses us from every sin.
So, while the water witnesses to Jesus’ birth, the blood witnesses to his death on the cross. The true testimony about Jesus, as we saw in 1 Jn 4:2-3, is a testimony to his humanity. The witness of the Spirit assumes Jesus’ divinity as Son of God, but apart from the incarnation, that truth is neither accessible nor relevant to us.

This is all very complicated and messy. God calls us, in each circumstance, to do the loving thing–but what does that mean? God’s testimony about Jesus is likewise messy, tied up inextricably with his, and our, humanity. Isn’t there a shortcut to discernment–something that just tells us straightforwardly what to do and say and believe?
Some would claim that there is: the Bible as the Word of God is our infallible guide and rulebook. Speaker of the House Mike Johnson told Fox News’ Sean Hannity:
I am a Bible-believing Christian. Someone asked me today in the media, they said, ‘People are curious, what does Mike Johnson think about any issue under the sun?’ I said, “Well, go pick up a Bible off your shelf and read it.” That’s my worldview.
I am sure, friends, that Mr. Johnson was sincere. But as it happens, the Scripture text we have been unpacking provides a ready critique of that claim. In the King James Bible of 1611, 1 John 5:6-8 reads as follows:
This is he that came by water and blood, even Jesus Christ; not by water only, but by water and blood. And it is the Spirit that beareth witness, because the Spirit is truth. For there are three that bear record in heaven, the Father, the Word, and the Holy Ghost: and these three are one. And there are three that bear witness in earth, the Spirit, and the water, and the blood: and these three agree in one.
The explicit reference to the Trinity in the KJV (boldfaced in the paragraph above) does not appear in the NRSVue, the CEB, the NIV, or indeed in any modern English translation of 1 John. That is not because of some conspiracy among Bible translators who do not believe in the Trinity! Rather, that verse is not found in the oldest and best texts of this book; in fact, it does not appear in any Greek text of 1 John before the 14th century!
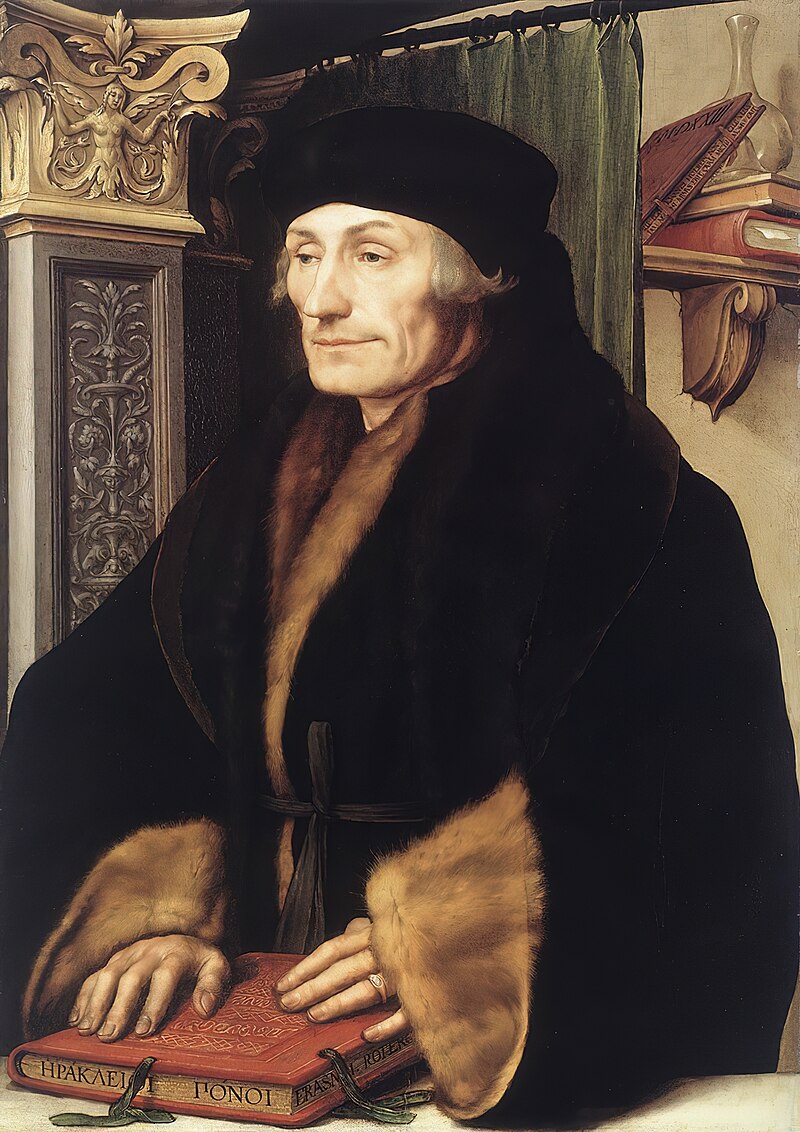

So, why does the KJV include it? King James’ 1611 translators were strongly influenced by Erasmus’ 1516 Textus receptus (“the received [and therefore presumably authoritative] text” of the Greek NT), and by the Latin Vulgate, where this verse does appear–but only in late (fourth century) Latin texts. Simply put, this neat Trinitarian confession does not belong to 1 John, but rather reflects later Christian reflection on that text. Modern translators are right to exclude it.
So, why am I telling you this? It certainly is not to persuade you that the Bible is unreliable, or that it isn’t the Word of God! Certainly, there was no deception involved on the part of the King James translators, or of Erasmus. Most likely, a Christian scribe copying the Latin text of 1 John, prompted by the mention of three witnesses in 1 Jn 5:6-9, added a note in the margin referencing the Trinity, and a later scribe included that note in the text itself–prompting still later scribes to add this to their Greek texts too, as Erasmus did.

Still, the point is that we do not have a single, pristine, “original” text of any biblical book, New Testament or Old–so responsible Bible scholars encounter this sort of problem all the time. Bible translators do not begin with how best and most faithfully to render the biblical languages into clear and understandable English. The prior question is which ancient version of a text to translate! Addressing that question requires expert knowledge–and even experts may disagree.
In short, friends, the Bible is no short cut, setting us free from our task of interpretation and discernment. The Bible, too, is messy and complicated. So being honest about how we read Scripture requires us to think hard and to pray hard on what exactly we do mean when we say that the Bible is word of God for people of God.
What if, instead of a rule book compelling our obedience, or a list of propositions requiring our assent, the Bible is an invitation into relationship with God, calling for our commitment? What if the Bible is a love letter from God–an invitation to open conversations, rather than an authoritative stopper that closes them? Then we will need to be guided in our reading as in our living by the principle of God’s love and by the example of Jesus, as we carefully and prayerfully listen for the Word among the words.
 Most of the time, we can comfortably live as though we are at the center of the universe. This month’s eclipse was a vivid reminder that we are not: that the universe is far larger, stranger, and more wonderful than our day-to-day experience may lead us to believe.
Most of the time, we can comfortably live as though we are at the center of the universe. This month’s eclipse was a vivid reminder that we are not: that the universe is far larger, stranger, and more wonderful than our day-to-day experience may lead us to believe.





 This week, as Christian pastors and laity alike turn in their devotions to reflection on Jesus’ betrayal, trial, torture, and death, it seems appropriate to turn to the witness of the apostle Paul, our first-century peer.
This week, as Christian pastors and laity alike turn in their devotions to reflection on Jesus’ betrayal, trial, torture, and death, it seems appropriate to turn to the witness of the apostle Paul, our first-century peer. So–when and how did Jesus send him? In
So–when and how did Jesus send him? In  Paul freely acknowledges that this is absurd on its face:
Paul freely acknowledges that this is absurd on its face: This means that the death of Jesus on the cross is not just about Jesus (
This means that the death of Jesus on the cross is not just about Jesus ( In our American date format, today is 3/14, which is also, as it happens, pi to the first two digits–making March 14 Pi Day! To refresh from high school geography, pi is the ratio between the circumference of a circle and its diameter–so, if you know the radius of a circle, you can use pi to calculate its circumference (2πr) or its area (πr squared: prompting the very bad pun, “No, pie are round; cornbread are square”). That ratio is, approximately, 3.14159–although mathematicians have now calculated its value out
In our American date format, today is 3/14, which is also, as it happens, pi to the first two digits–making March 14 Pi Day! To refresh from high school geography, pi is the ratio between the circumference of a circle and its diameter–so, if you know the radius of a circle, you can use pi to calculate its circumference (2πr) or its area (πr squared: prompting the very bad pun, “No, pie are round; cornbread are square”). That ratio is, approximately, 3.14159–although mathematicians have now calculated its value out 




 Evangelical pastor and author Brian Zahnd is concerned that much of American Christianity today is characterized, not by service or kindness, but by fear and anger–even hatred. Challenging his fellow pastors and leaders, Zahnd says,
Evangelical pastor and author Brian Zahnd is concerned that much of American Christianity today is characterized, not by service or kindness, but by fear and anger–even hatred. Challenging his fellow pastors and leaders, Zahnd says,
 Once again (it happened in 2018, too, remember!) Ash Wednesday falls on Valentines Day. Certainly the contrast– the sweetest and most sentimental of secular holidays juxtaposed with the grimmest and most lugubrious of Christian fast days–is striking, and may prompt us to wonder why the church should be such a downer–so determined, it seems, to quash anything fun.
Once again (it happened in 2018, too, remember!) Ash Wednesday falls on Valentines Day. Certainly the contrast– the sweetest and most sentimental of secular holidays juxtaposed with the grimmest and most lugubrious of Christian fast days–is striking, and may prompt us to wonder why the church should be such a downer–so determined, it seems, to quash anything fun.


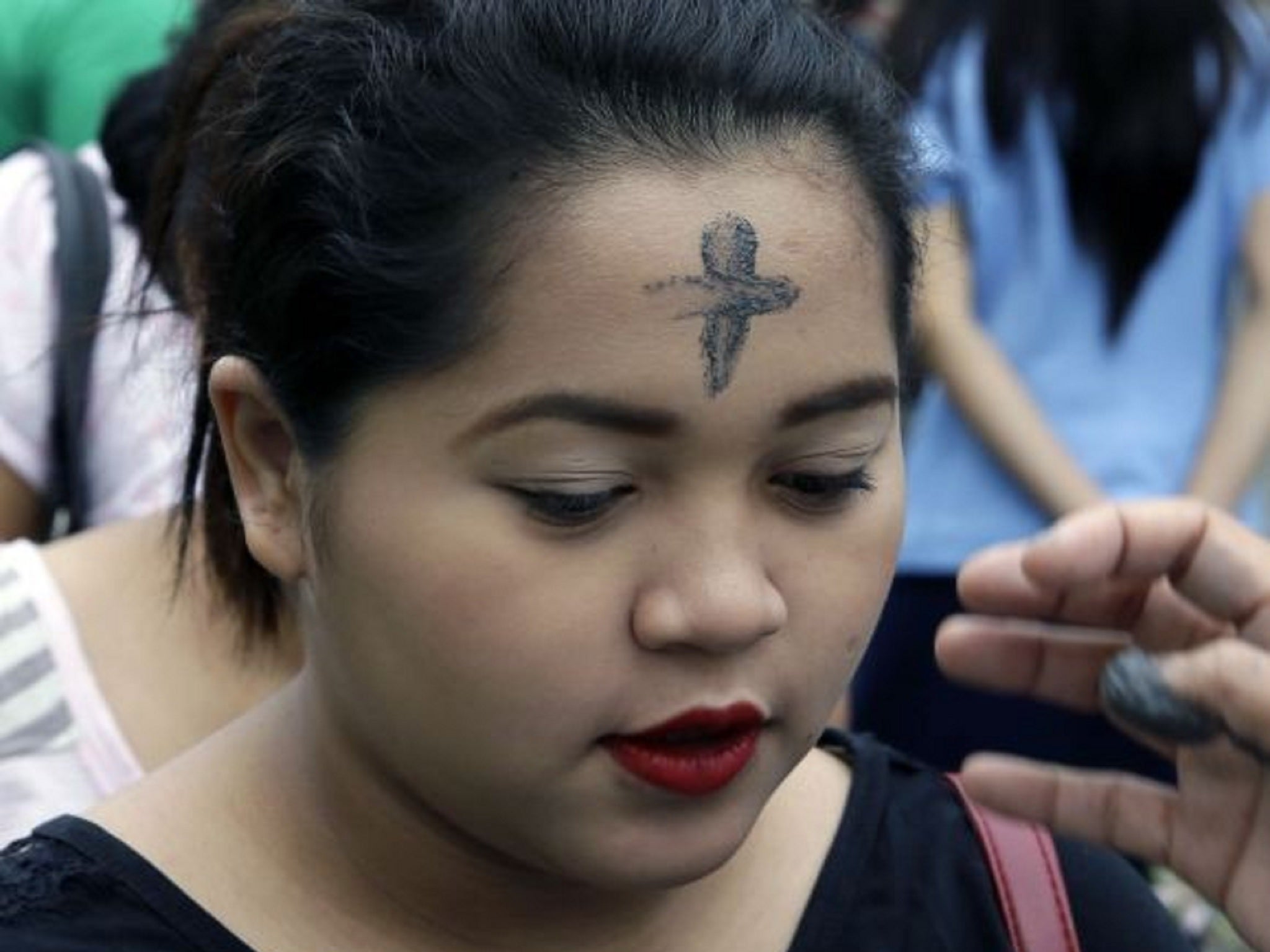

 I learned of this piece through a concert at my home church, St. Paul’s UMC, by Archipelago, an extraordinary vocal ensemble conducted by Caron Daley of Duquesne University. The climax of the evening was a wonderful choral setting of DuBois’ “Credo” by African American composer
I learned of this piece through a concert at my home church, St. Paul’s UMC, by Archipelago, an extraordinary vocal ensemble conducted by Caron Daley of Duquesne University. The climax of the evening was a wonderful choral setting of DuBois’ “Credo” by African American composer 




 This day, in the dead of winter, is associated with hope for the return of warmer weather–but not too soon. A “false spring” after all may be followed by a killing frost, wiping out trees that have budded too early, and threatening lambs born out of season. Therefore, sunny weather on this midwinter day (so that a groundhog can see its shadow!) is held to be a bad omen of more bleak days ahead, while cold and cloudy weather appropriate to the season augurs the swift return of sunshine and greenery.
This day, in the dead of winter, is associated with hope for the return of warmer weather–but not too soon. A “false spring” after all may be followed by a killing frost, wiping out trees that have budded too early, and threatening lambs born out of season. Therefore, sunny weather on this midwinter day (so that a groundhog can see its shadow!) is held to be a bad omen of more bleak days ahead, while cold and cloudy weather appropriate to the season augurs the swift return of sunshine and greenery.![Title: Presentation in the Temple [Click for larger image view]](http://diglib.library.vanderbilt.edu/cdri/jpeg/C_FirstSundayafterChristmas.jpg) This tapestry depicting Luke’s scene is from the Abbey Church of St. Walpurga in Virginia Dale, Colorado. The Order of St. Walpurga was established in the 11th century in Bavaria. The nuns of that order fled to the United States in 1935 to escape the Nazis, and settled in the Colorado mountains. The walls of their church are lined with tapestries like this one of the Presentation of the Lord, all inspired by biblical texts.
This tapestry depicting Luke’s scene is from the Abbey Church of St. Walpurga in Virginia Dale, Colorado. The Order of St. Walpurga was established in the 11th century in Bavaria. The nuns of that order fled to the United States in 1935 to escape the Nazis, and settled in the Colorado mountains. The walls of their church are lined with tapestries like this one of the Presentation of the Lord, all inspired by biblical texts. Although Jesus has come for everyone, not everyone will receive him. Simeon’s words prefigure Jesus’ coming rejection–his trial, condemnation, and crucifixion, and so Mary’s coming sorrow: “And a sword will pierce your innermost being too” (Luke 2:35). In this season after Epiphany, we rightly remember that Jesus’ way leads us to God’s light–but that way must pass through the darkness of the cross. Simeon offers no illusions that God’s salvation comes easily, without opposition or conflict.
Although Jesus has come for everyone, not everyone will receive him. Simeon’s words prefigure Jesus’ coming rejection–his trial, condemnation, and crucifixion, and so Mary’s coming sorrow: “And a sword will pierce your innermost being too” (Luke 2:35). In this season after Epiphany, we rightly remember that Jesus’ way leads us to God’s light–but that way must pass through the darkness of the cross. Simeon offers no illusions that God’s salvation comes easily, without opposition or conflict.






